17.JDBC、连接池
大约 14 分钟学习笔记Java基础
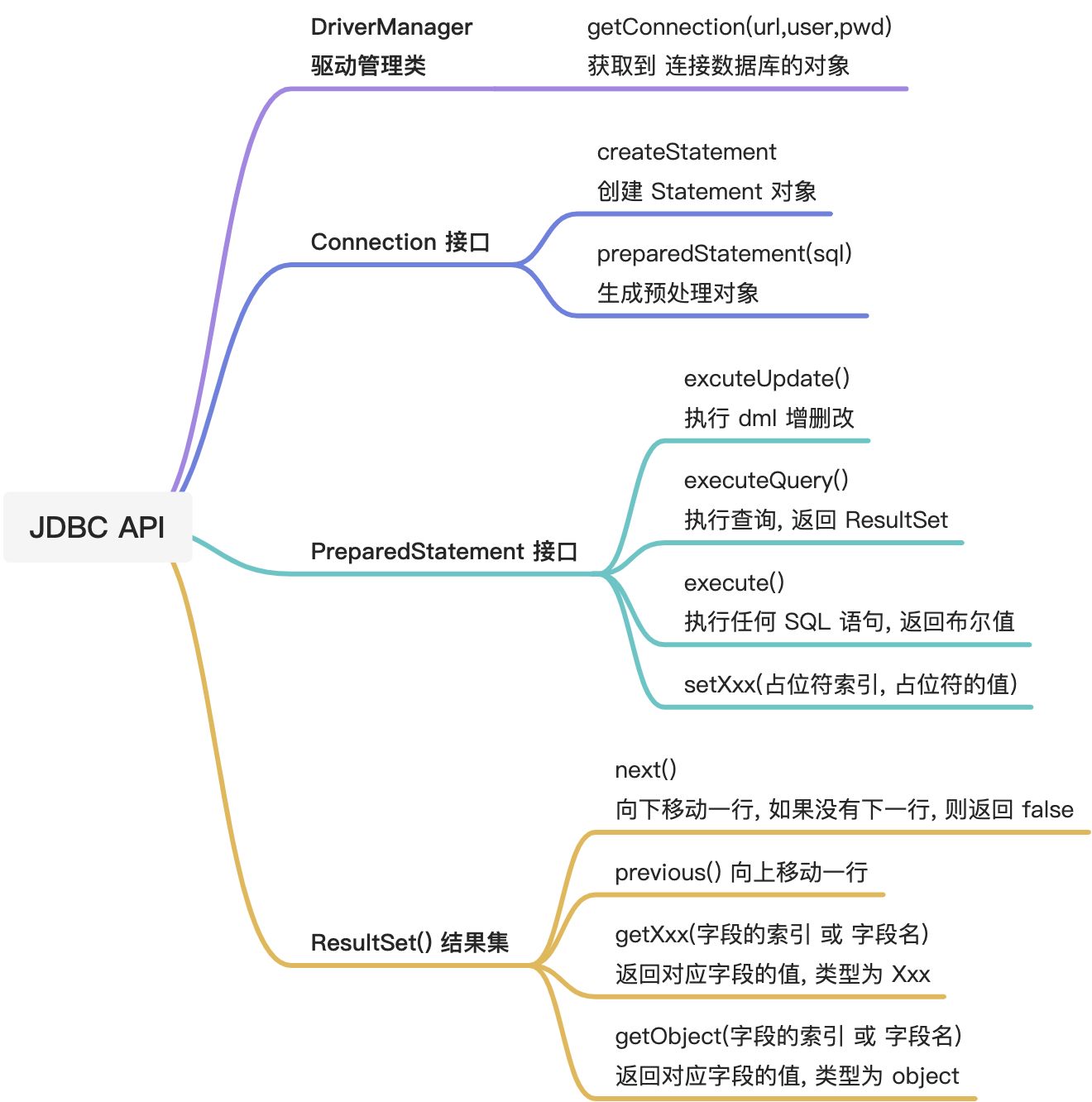
一. JDBC
JDBC 为访问不同的数据库提供了统一的接口, 为使用者屏蔽了细节问题; Java 程序员试用 JDBC, 可以连接任何提供了 JDBC 驱动程序的数据库系统, 从而完成对数据库的操作
MySQL 驱动下载 : https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/j/
提示
JDBC 程序编写步骤:
- 注册驱动 : 加载 driver 类
- 在项目中创建 libs 文件夹, 将 mysql.jar 拷贝到该目录下, 将 jar 文件 添加到项目中
- 获取连接 : 得到 Connection
- jdbc:mysql : 表示规定好的协议, 通过 jdbc 连接 MySQL
- localhost : 表示 ip 地址
- 3306 : 表示监听的端口
- 执行增删改查 : 发送 sql 给 mysql 执行
- 释放资源 : 关闭相关连接
1. 数据库连接方式
// 数据库连接方式
public class MysqlDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
}
// 方式 1 - 使用 Class.forName 自动完成注册驱动
@Test
public void connect4() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
// 使用反射加载 Driver 类
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_02";
String user = "root";
String password = "12345678";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
// 方式 2 - 增加配置文件
@Test
public void connect5() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException, IOException {
String filePath = new File("").getAbsolutePath()+"/src/mysql.properties";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream(filePath));
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
Class.forName(driver);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
}// 配置文件 - mysql.properties
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_02
user=root
password=123456782. 操作数据库
// 操作数据库
public class HomeWork1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("./src/mysql.properties"));
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
// 1. 加载驱动, 可以不写, 底层自动加载
Class.forName(driver);
// 2. 连接数据库
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// 3. 得到 statement 对象, 用于执行 SQL 语句, 并返回对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql_newTable = "create table news(id int primary key auto_increment, `name` varchar(32) not null default '')";
int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql_newTable);
System.out.println(i > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
String sql_insert = "insert into news values(null, '张三'),(null, '李四'),(null, '王五'),(null, '赵六')";
int i1 = statement.executeUpdate(sql_insert);
System.out.println(i1 > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
String sql_update = "update news set `name` = '张三疯' where id = 3";
int i2 = statement.executeUpdate(sql_update);
System.out.println(i2 > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
String sql_delete = "delete from news where id = 4";
int i3 = statement.executeUpdate(sql_delete);
System.out.println(i3 > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
connection.close();
statement.close();
}
}3. PreparedStatement
注
Statement 对象 : 用于执行 SQL 语句, 并返回其生成的结果对象;
执行 SQL 语句可以通过以下方式:
- Statement : 存在 SQL 注入的问题
- PreparedStatement : 预处理, 实际工作中使用
- 不用拼接 SQL 语句, 减少语法错误
- 预防 SQL 注入问题
- 减少编译次数, 效率较高
- CallableStatement : 存储过程
注意
- Statement 对象执行 SQL 语句时, 存在 SQL 注入的风险;
- SQL 注入 : 利用某些系统没有对用户输入的数据进行充分的检查, 而在用户输入数据中注入非法的 SQL 语句断货命令, 恶意攻击数据库;
提示
- PreparedStatement : 用于执行 SQL 语句, 规避 SQL 注入的风险
- 执行 SQL 语句中的 参数 可以用 ? 来表示;
- 调用 对象的 setXxx(参数 1, 参数 2) 方法来设置这些参数;
- 参数 1 : 表示要设置 SQL 语句中的第几个参数 (第几个问号), 从 1 开始;
- 参数 2 : 表示要设置的参数值;
- 调用 executeQuery() 方法, 返回 ResultSet 对象;
- 调用 executeUpdate() 方法 : 执行 SQL 语句的 增, 删, 改;
public class MysqlDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("./src/mysql.properties"));
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
// 1. 加载驱动, 可以不写, 底层自动加载
Class.forName(driver);
// 2. 连接数据库
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// 3. 获取 preparedStatement 对象
String sql = "select * from news where `name` = ?";
// preparedStatement 实现了 PreparedStatement 接口
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 给 ? 赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1,"张三");
// 4. 执行 SQL 语句
// 如果执行 增 删 改 语句, 则需要 executeUpdate() 方法
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
String string = resultSet.getString(1);
System.out.println(string);
}
// 5. 关闭
resultSet.close();
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
}4. JDBCUtils 封装及使用
封装 jdbcUtils
// JdbcUtils 封装
public class JdbcUtils {
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static String url;
private static String driver;
public static void loadFile(String filePath){
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
// 读取配置文件
properties.load(new FileInputStream(filePath));
user = properties.getProperty("user");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
} catch (IOException e) {
// 实际开发中, 会将编译异常转换为 运行异常
// 开发者可以选择 捕获异常 或者 选择默认处理异常
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static Connection getConnection(){
try {
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void close(ResultSet set, Statement statement, Connection connection){
try {
if (set != null){
set.close();
}
if (statement != null){
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null){
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}// JdbcUtils 调用 - 案例
public class MysqlTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
selectTest();
}
public static void selectTest(){
// 读取文件, 创建连接
JdbcUtils.loadFile("./src/mysql.properties");
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from news";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 执行 SQL 语句
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while(resultSet.next()){
String id = resultSet.getString("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
System.out.println(id + " " + name);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭资源
JdbcUtils.close(resultSet, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
public void dmlTest(){
// 读取文件, 创建连接
JdbcUtils.loadFile("./src/mysql.properties");
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into news values(null, '郭富城')";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
// 执行 SQL 语句
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭资源
JdbcUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
}5.事务
提示
- JDBC 程序中, 当一个 connection 对象创建时, 默认情况下是 自动提交事务;
- 每次执行 SQL 语句时, 成功则自动完成提交, 不能回滚;
- JDBC 程序中, 可以使用事务, 将多个 SQL 语句作为一个整体执行;
- 调用 Connection 的 setAutoCommit(false) 可以取消自动提交事务;
- 在所有 SQL 语句执行成功后, 调用 connection 的 commit() 方法 提交事务
- 在其中某个操作失败或出现异常时, 调用 connection 的 rollback() 方法回滚事务;
// 事务 - 案例
public class MysqlTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
transfer();
}
// 创建 表
public static void createTable(){
JdbcUtils.loadFile("./src/mysql.properties");
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql_createTable = "create table account(id int primary key auto_increment, `name` varchar(32)not null default '', balance double not null default 0)character set utf8";
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql_createTable);
boolean execute = statement.execute();
System.out.println(execute ? "创建表失败" : "创建表是成功");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.close(null, statement, connection);
}
}
// 添加数据
public static void insertInto(){
JdbcUtils.loadFile("./src/mysql.properties");
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql_insert = "insert into account values(null, '刘德华', 3000), (null, '王宝强', 500)";
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql_insert);
boolean execute = statement.execute();
System.out.println(execute);
System.out.println(!execute ? "添加成功" : "添加失败");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.close(null, statement, connection);
}
}
public static void transfer(){
JdbcUtils.loadFile("./src/mysql.properties");
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql_update1 = "update account set balance = balance - 1000 where `name` = '刘德华'";
String sql_update2 = "update account set balance = balance + 1000 where `name` = '王宝强'";
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
// 关闭 事务自动提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
// 执行第一条 sql
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql_update1);
statement.execute();
// 故意制造错误, 查看 数据是否异常
// int i = 1 / 0;
// 执行第二条 sql
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql_update2);
statement.execute();
// 提交事务
connection.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
try {
System.out.println("转账执行失败, 回滚到事务开始");
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.close(null, statement, connection);
}
}
}6. 批量处理
注
- 当需要批量插入或更新记录时, 可以采用 Java 的批量更新机制;
- 将多条 sql 语句 一次性交给数据库, 比单条提交更有效率;
- JDBC 批量处理语句的方法:
- addBatch() : 添加需要批量处理的 sql 语句或参数;
- executeBatch() : 执行批量处理包的语句;
- clearBatch() : 清空批量处理包的语句;
- JDBC 连接 mysql 时, 如果要使用批量处理功能, 需要 在 URL 中加参数
- ?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
- 批量处理 一般和 PreparedStatement 搭配使用, 可以减少编译次数,运行次数;
// 配置更新 - ?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_02?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
user=root
password=12345678// 批量处理 - 案例
public class BatchDemo1 {
@Test
public void batch() throws Exception {
JdbcUtils.loadFile("./src/mysql.properties");
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into admin2 values(null, ?, ?)";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
System.out.println("开始执行");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
statement.setString(1,"jack" + i);
statement.setString(2, "123");
// 将 SQL 语句加入到批量处理包中
statement.addBatch();
// 当 有 1000 条语句时, 执行 SQL 语句
if ((i + 1) == 1000){
// 执行批量处理包
statement.executeBatch();
// 清空批量处理包
statement.clearBatch();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行结束, 共计耗时 : " + (end - start) );
JdbcUtils.close(null,statement,connection);
}
}二. 连接池
注
- 预先在缓冲池中放入一定数量的连接, 当需要连接数据库时, 只需取出一个, 使用完毕之后再放回去
- 数据库连接池 负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接;
- 连接池 允许应用程序 重复使用 一个现有的数据库连接, 而不是重新建立一个;
- 当应用程序向连接池请求的连接数超过最大连接数时, 将加入到等待队列中;
提示
- JDBC 的数据库连接池使用 javax.sql.DataSource 来表示;
- DataSource 只是一个接口, 该接口通常由第三方提供实现;
连接池的种类:
- C3P0 连接池 : 速度较慢, 稳定性较好;
- DBCP 连接池 : 速度 相对 C3P0 较快, 稳定性较差;
- Proxool 连接池 : 有监控连接池状态的功能, 稳定性较差;
- BoneCP 连接池 : 速度快
- **Druid (德鲁伊) 连接池 **: 阿里提供的连接池, 集 DBCP、C3P0、Proxool 优点于一身
1. 环境配置
提示
- 下载 Druid 的 jar 包, 放入 libs 文件夹, 右键 jar 包 添加为库;
- 下载 配置文件, 放入 src 文件夹下
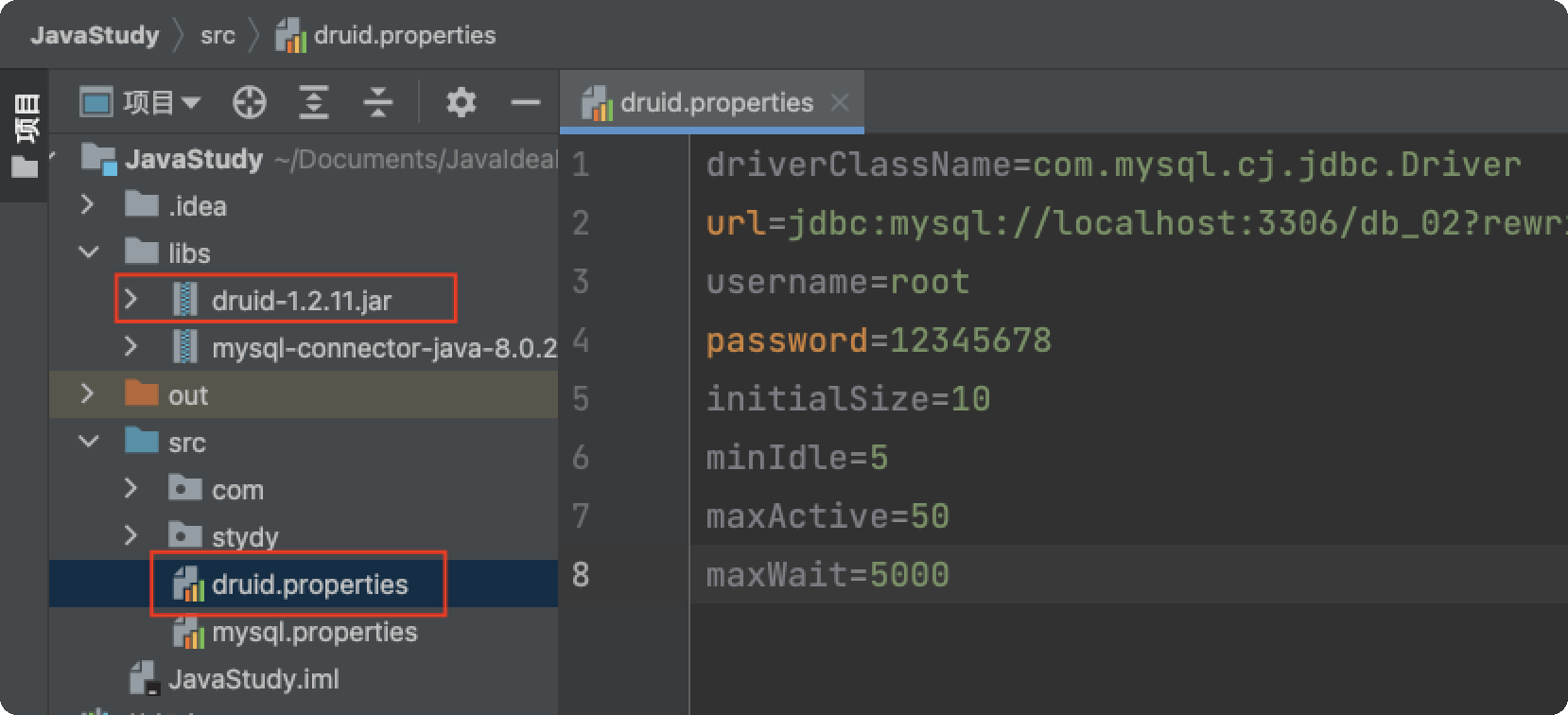
// 配置文件 - druid.properties
# 数据库驱动
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_02?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
username=root
password=12345678
# 初始化连接数
initialSize=10
# 最小连接数
minIdle=5
# 最大连接数
maxActive=20
# 最大连接等待时间 单位毫秒
maxWait=5000// druid 连接 - 案例
public class DruidDemo1 {
@Test
public void druidTest1() throws Exception {
// 1. 创建 Properties 对象, 读取配置文件
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
// 2. 创建一个指定参数的数据库连接池, druid 连接池
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
// 3. 连接数据库
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println("连接成功");
// 4. 关闭连接
connection.close();
}
}2. JDBCUtilsByDruid 封装及使用
// JDBCUtilsByDruid 封装
public class JDBCUtilsByDruid {
private static DataSource ds;
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
// 读取配置文件
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\druid.properties"));
// 创建 druid 连接池
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取数据库连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();
}
// 关闭连接(断开连接, 放回连接池)
public static void close(ResultSet set, Statement statement, Connection connection){
try {
if (set != null){
set.close();
}
if (statement != null){
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null){
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}// JDBCUtilsByDruid 使用 案例
public class DruidDemo2 {
@Test
public void druidTest1(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
String sql = "select * from actor";
try {
connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
String sex = resultSet.getString("sex");
String borndate = resultSet.getString("borndate");
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
System.out.println(id + name + sex + borndate + phone);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(resultSet, statement, connection);
}
}
}3. DBUtils 工具类
注
DBUtils 类:
- QueryRunner 类 : 该类封装了 sql 的执行, 是线程安全的;
- 可以实现 增、删、改、查、批量处理
- ResultSetHandler 接口 : 该接口用于处理 java.sql.ResultSet, 将数据按要求转换为另一种形式;
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ArrayHandler | 把 结果集 中的第一行数据转成 对象数组; |
| ArrayListHandler | 把 结果集 中的每行数据都转成一个数组, 再存放到 list 中 |
| BeanHandler | 将 结果集 中的第一行数据封装到一个对应的 JavaBean 实例中 |
| BeanListHandler | 将 结果集 中的每一行数据都封装到一个对应的 JavaBean 实例中,存放到 list 里 |
| ColumnListHandler | 将 结果集 中的某一列的数据存放的 List 中 |
| KeyedHandler(name) | 将 结果集 中的每行数据都封装到 map 里, |
| MapHandler | 将 结果集 中的第一行数据封装到一个 Map 里, key 为列名, values 对应值 |
| MapListHandler | 将 结果集 中的每行数据都封装到一个 Map 里, 然后放到 L 冲突 |
注意
- 下载 DBUtils 的 jar 包, 解压获取 commons-dbutils-xx.jar 文件
- 将 commons-dbutils-xx.jar 文件放入 libs 文件夹
- 右键点击该文件, 添加到库
// 创建数据库表 的类
public class Actor {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private Date borndate;
private String phone;
public Actor() { //一定要给一个无参构造器[反射需要]
}
public Actor(Integer id, String name, String sex, Date borndate, String phone) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.borndate = borndate;
this.phone = phone;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Date getBorndate() {
return borndate;
}
public void setBorndate(Date borndate) {
this.borndate = borndate;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "\nActor{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", borndate=" + borndate +
", phone='" + phone + '\'' +
'}';
}
}// Druid + DBUtils 案例
public class DBUtilsDemo1 {
@Test
public void testQueryMany() throws SQLException {
// 1. 获取 连接
Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
// 2. 创建 QueryRunner
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
// 3. 执行相关方法, 返回 list 集合
String sql = "select * from actor where id >= ?";
// query 方法执行 sql 语句, 将得到的结果封装到 ArrayList 中
// new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class) : 将 resultSet 转为 Actor 对象 分装到 ArrayList 中
// 底层会自动关闭 query 和 statement
List<Actor> actorList = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class), 1);
for (Actor actor : actorList) {
System.out.println(actor);
}
// 关闭连接 -
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection);
}
}// queryRunner 增删改 - 案例
@Test
public void testQueryDml() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql_insert = "insert into actor values(null, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
String sql_update = "update actor set name = ? where id = ?";
String sql_delete = "delete from actor where id = ?";
// 执行结果返回修改了多少行, 修改失败返回 0
int insert = queryRunner.update(connection, sql_insert, "虚竹", "男", "1999-11-23", "13243435656");
int update = queryRunner.update(connection, sql_update, "完颜洪烈", 2);
int delete = queryRunner.update(connection, sql_delete, 6);
System.out.println(insert > 0 ? "修改成功" : "修改失败");
System.out.println(update > 0 ? "修改成功" : "修改失败");
System.out.println(delete > 0 ? "修改成功" : "修改失败");
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection);
}4. DAO 和 增删改查通用方法 - BasicDao
注
- DAO : 数据访问对象
- BasicDao : 专门和数据库交互, 即完成对数据库表的 crud 操作;
- 在 BaicsDao 的基础上, 实现一张表 对应 一个 Dao, 更好的完成功能;
- 如 Customer 表 ---> Customer.java 类(javabean) ---> CustomerDao.java
// utils.JDBCUtilsByDruid.java (工具包中的 druid 封装)
public class JDBCUtilsByDruid {
private static DataSource ds;
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
// 读取配置文件
properties.load(new FileInputStream("./src/druid.properties"));
// 创建 druid 连接池
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取 数据库连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();
}
// 断开连接, 释放资源
public static void close(Connection connection){
if (connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}//d omain.Actor.java (将数据库表封装成类))
public class Actor {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private Date borndate;
private String phone;
public Actor() {
}
public Actor(Integer id, String name, String sex, Date borndate, String phone) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.borndate = borndate;
this.phone = phone;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public Date getBorndate() {
return borndate;
}
public void setBorndate(Date borndate) {
this.borndate = borndate;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Actor{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", borndate=" + borndate +
", phone='" + phone + '\'' +
'}';
}
}// dao.BasicDao.java (表 操作方法 基类封装)
public class BasicDao<T> {
private final QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner();
/**
* 增、删、改 操作方法
* @param sql : SQL 语句
* @param parameters : SQL 语句中的 ? 对应的具体的值, 可以有多个
* @return : 返回有多少行数据发生了改变, 0 表中数据没有发生改变
*/
public int dml(String sql, Object... parameters) {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
return qr.update(connection, sql, parameters);
} catch (SQLException e) {
// 编译异常改为 运行异常
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(connection);
}
}
/**
* 查询语句返回 多行 结果
* @param sql : SQL语句
* @param clazz : 传入一个类的 class 对象, 如 Actor.class
* @param parameters : 传入 SQL 语句中 ? 具体的值, 可以有多个
* @return : ArrayList 集合
*/
public List<T> queryMulti(String sql, Class<T> clazz, Object... parameters) {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
return qr.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<T>(clazz), parameters);
} catch (SQLException e) {
// 编译异常改为 运行异常
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(connection);
}
}
/**
* 查询语句返回 单行 结果
* @param sql : SQL语句
* @param clazz : 传入一个类的 class 对象, 如 Actor.class
* @param parameters : 传入 SQL 语句中 ? 具体的值, 可以有多个
* @return : 返回 类型对象
*/
public T querySingle(String sql, Class<T> clazz, Object... parameters) {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
return qr.query(connection, sql, new BeanHandler<>(clazz), parameters);
} catch (SQLException e) {
// 编译异常改为 运行异常
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(connection);
}
}
/**
* 查询 单个字段 的值
* @param sql : SQL 语句
* @param parameters : 传入 SQL 语句中 ? 具体的值, 可以有多个
* @return : 返回 单个字段的值
*/
public Object queryScalar(String sql, Object... parameters){
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
return qr.query(connection, sql, new ScalarHandler<>(), parameters);
} catch (SQLException e) {
// 编译异常改为 运行异常
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(connection);
}
}
}// dao.ActorDao.java (单个表操作方法封装, 主要存放表特定的操作方法)
public class ActorDao extends BasicDao<Actor> {
}// test.TestDaoDemo1 (操作 - 案例)
public class TestDaoDemo1 {
@Test
public void testActorDao1() {
ActorDao actorDao = new ActorDao();
// 多行查询
List<Actor> list = actorDao.queryMulti("select * from actor where id >= ?", Actor.class, 2);
System.out.println("=====多行查询=====");
for (Actor actor : list) {
System.out.println(actor);
}
// 单行查询
Actor actor = actorDao.querySingle("select * from actor where id = ?", Actor.class, 2);
System.out.println("单行查询 : " + actor);
// 单个字段查询
Object o = actorDao.queryScalar("select name from actor where id = ?", 2);
System.out.println("单个字段值查询 : " + o);
// 增
int dml = actorDao.dml("insert into actor values(null, ?,?,?,?)", "马云", "男", "1956-1-12", "88889999");
System.out.println(dml > 0 ? "添加成功" : "添加失败");
// 改
int dml1 = actorDao.dml("update actor set name = ? where name = ?", "马化腾", "马云");
System.out.println(dml1 > 0 ? "修改成功" : "修改失败");
// 删
int dml2 = actorDao.dml("delete from actor where name = ?", "马云");
System.out.println(dml > 0 ? "删除成功" : "删除失败");
}
}